Home » battery news » Interpretation of China’s power battery recycling industry
Interpretation of China's power battery recycling industry
Since 2018, every year it has been said that it is the first year of power battery recycling. However, the power battery recycling market has not really exploded so far.
However, everyone believes that the power battery will eventually be retired. The recycling industry is like a cornucopia, which will surely gather hundreds of billions of trillions of wealth.
What was the status quo of the industry before the explosion of such a trillion-dollar market? This article will give you a comprehensive and in-depth analysis.
Small workshops and formal recycling companies
Power battery recycling begins with the promotion of new energy vehicles.
However, it was not retired batteries that were recycled at the beginning. In the early stage of the promotion of new energy vehicles, the power battery manufacturing technology was very immature, and the yield rate was low. A number of small workshops were spawned in China to recycle waste battery cell materials.
Later, recyclers began to collect waste batteries with high residual capacity and good detection indicators, and sold them at the price of cascade utilization; after bad manual dismantling, they were sold to downstream smelting enterprises to extract cathode material precursors.
During this period, small workshops were the main force of battery recycling.
With the continuous promotion of new energy vehicles, the recycling of retired batteries has gradually been paid attention to by government departments of various countries. Due to the possible pollution to the environment, there may also be potential safety hazards.
Therefore, the Chinese government has implemented a whitelist system for power battery recycling, and thus there are formal recycling companies for battery recycling.
China’s power battery recycling companies have registered from more than 300 in 2017 to nearly 3,000 in 2021, but currently there are only 45 companies that meet the industry standards set by the Chinese government.
Many of these companies have great backgrounds. For example, Bangpu Cycle, Huayou Cycle, GEM, and Ganzhou Highpower have entered the “white list” of the first batch of battery recycling by virtue of their early 3C lithium cobalt oxide battery recycling and qualifications for hazardous waste treatment.
Behind Bangpu is the Ningde era, Huayou has mines and is a leader in cobalt smelting, GEM is the leader of ternary precursors, and there is a car dismantling network.
Of course, there’s no shortage of startups on the list who see power battery recycling opportunities and join in.
During the epidemic in early 2020, Shenzhen Bus Group started the decommissioning of the first batch of new energy buses, with a total of more than 200 vehicles and more than 700 tons of batteries.
Hengchuangrui was able to bid for the battery and won the largest order in the history of power battery recycling. Saidmei can be called a model worker in the industry. In the absence of funds and little background, it has also become one of the whitelists for battery recycling with its material repair technology.
With the emergence of regular recycling companies, is power battery recycling on the right track? Let’s first calculate how many power batteries can be recycled.
According to the annual installed capacity of new energy vehicles, according to the battery energy density of 120wh/kg, it will be retired and recycled after 4 years of use, and the scale of retired batteries will be roughly calculated.
About 240,000 tons of power batteries will be retired in 2020. Where did the 240,000 flow go? According to industry statistics, the recycling volume of formal recycling enterprises is less than 50,000 tons.
In 2021, the overall recycling scale of each company will increase, and some recycling scales will double, but due to factors such as the total amount of retired batteries, prices, and long-distance transportation, the recycling volume of several leading companies is no more than 10,000 tons, and most of the retired power batteries still flow into small workshops for on-site recycling.
All parties tried their best to recycle batteries, but because the bidding for used batteries is the highest price, small workshops often dare to bid because they are not responsible for environmental protection and have low disposal costs.
The phenomenon that formal recycling enterprises are collect less batteries still exists.
Formal recycling companies not only collect less batteries, but also have difficulty making profits.
Policy orientation is not enough
In China, it is not reasonable to choose a recycling party by auctioning waste batteries with the highest price.
Many European and American countries have passed legislation to establish a complete legal and regulatory system for the recycling of waste materials, clarify the penalties for illegal operations, and cooperate with the “deposit system” to recycle batteries.
Japan implements reverse recycling, advocating citizens to voluntarily make efforts to return used batteries to battery manufacturers, and then hand them over to professional battery recycling companies for disposal.
In many countries, used batteries are classified as hazardous waste, and the holder cannot only use it to sell for money, but also needs to pay battery recycling companies for harmless treatment.
For Umicore, a world-renowned material company, the price of a combustion furnace for battery recycling is as high as 1 billion yuan. It can be seen that the cost of recycling is high, and the government and enterprises attach great importance to environmental protection.
Therefore, policy guidance is indeed needed to pay attention to the huge social cost of battery recycling and take strict control measures.
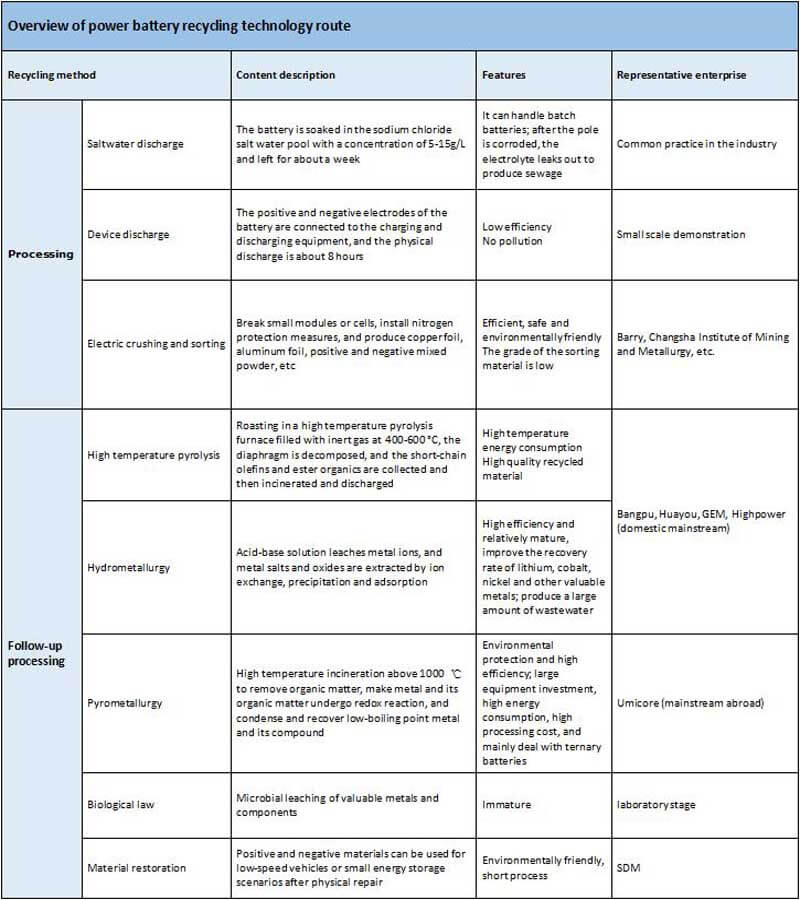
Technical route
Power batteries have different standards and models, which brings difficulties to the cascade utilization and recycling of batteries. Cascade utilization requires dismantling, testing, volume distribution, and reorganization, mainly manual and semi-automatic.
Recycling can be divided into pretreatment and subsequent treatment. The pretreatment process is divided into discharge dismantling and charged crushing. After electrified crushing, copper foil, aluminum foil, black powder, shell, diaphragm and other materials are sorted out. Subsequent treatments include high temperature pyrolysis, hydrometallurgy, pyrometallurgy, material repair, etc.
The power battery recycling industry is still in the early stage of development, and there are countless recycling methods being researched, but nothing more than the above technical routes.
Under these current technical routes, the material recovery rate and industry standards require that the comprehensive recovery rate of nickel, cobalt, and manganese should not be less than 98%, the recovery rate of lithium should not be less than 85%, and the comprehensive recovery rate of other major valuable metals such as rare earth. Not less than 97%.
Of course, the higher the recovery rate, the better. However, improving the recovery rate not only requires its own technical skills, but also depends on the grade of materials in the pretreatment stage.
Taking lithium iron phosphate batteries as an example, the market demand for broken black powder is greater than 2.5% lithium content, preferably 3.8%. The positive and negative electrode sheets are manually disassembled, and the lithium content of pure positive electrode powder can easily reach the highest standard, while the lithium content after mechanical crushing into positive and negative electrode mixed powder is basically below 3.0%.
This leads to the phenomenon of bad money driving out good money. A large number of batteries are recycled by small workshops and manually disassembled into shells, copper foils, aluminum foils, and black powder. There are many formal recycling companies that outsource the batteries to small workshops for dismantling and pretreatment, and then recycle materials by hydrometallurgy.
Low-cost, high-value recycling is the advantage of small workshops. The cost of manual dismantling and sorting of 1 ton of batteries is 600 yuan, which is less than half of the cost of equipment dismantling and sorting in regular recycling enterprises. Of course, the price is at the expense of the environment and personal health. I sincerely hope that the state will establish supervision and management system measures as soon as possible to truly realize the harmless and orderly recycling of power batteries.
The technical route of power battery recycling is also evolving, because the technical route of power battery has not yet been finalized. In the early stage of development, nickel-metal hydride batteries, lithium manganate, lithium iron phosphate, ternary lithium, lithium titanate and other batteries in power batteries showed their magical powers and were all commercialized.
Later, lithium iron phosphate and ternary lithium batteries became the absolute mainstream due to their strong performance advantages. However, ternary battery safety accidents occur frequently. By 2021, lithium iron phosphate has become the main choice for power batteries.
Development continues. It is expected that in the next 3-5 years, semi-solid batteries will begin to be applied on a large scale. In the next 10 years, solid-state batteries are expected to occupy a place. Following these changes, battery recycling technology and equipment will face greater challenges.
Business model to be improved
To establish a business model for power battery recycling, we must first have a good recycling source. There are few battery packs that can be recycled but can be recycled from the main engine factory, ranging from a few to dozens of batteries, most of which have the value of cascade utilization. After the violent experiment of individual vehicles, the battery can be directly recycled if it is burned or damaged.
Another good source of recycling is to recycle pole piece scraps, non-liquid-injected cells, B-grade C-grade cells, battery packs, etc. from the battery factory.
The market channel of the pole piece material is stable and difficult to shake. The battery of the B grade and the C grade can be used as a cascade utilization battery for low-speed vehicles, two-wheeled vehicles, backup power supplies, street lamps, charging treasures, etc., and the market demand is very large.
Other ideal recycling sources are the decommissioned new energy bus batteries of bus companies, and hundreds of tons of lithium iron phosphate batteries can be recycled from a batch of decommissioned vehicles. Recycling companies bid for batteries, and the price ranges from 100 to 200 yuan per kilowatt-hour depending on the year of production, brand, and state of the battery.
On-site manual dismantling and pulling back to the factory for inspection and sorting, usually 80% can be used in cascade, and sold to enterprises or traders of cascade utilization at a price of 200 to 300 yuan.
Of course, the price of lithium carbonate continues to soar, and battery-grade lithium carbonate has risen to 400,000 yuan / ton. Now the recycling price also needs to consider the value of recycling.
Power batteries on new energy vehicles scrapped by car dismantling plants are also popular. In 2018, more than 1,000 new energy vehicles were scrapped at the dismantling plant, and 80% had batteries; in 2019, the automobile dismantling plant also recycled more than 1,000 new energy vehicles, and 80% of the vehicle batteries were dismantled and auctioned ahead of schedule.
Before the real cascading and recycling enterprises, there are also traders passing through. Traders are good at back-to-back sales, find battery sources, inquire about battery status and price range and other information, prepare to bid after on-site inspection and verification, and look for buyers at the same time.
The purchase of used batteries is a cash transaction, and the payment is delivered, and it is never in arrears, but the profit is the difference. The most diligent salesmen even drive their private cars to sweep the streets. Repair shops, scrap shops, and electric vehicle dealers are their frequent bases.
After getting a good source of goods, how can a real recycling company make money? The battery recycling business of small workshops is flexible and has many routines, at the expense of the environment and personal safety of employees, which will not be described in detail here.
Although formal recycling companies can reach strategic cooperation with OEMs and battery factories, and some foreign-funded car companies will provide battery treatment for free, the recycling volume is limited, and the existing business model is still difficult to make profits.
There are also new business models.
In order to lock the source of batteries in advance and recycle them in batches, recycling companies have begun to deploy battery swap businesses. The battery swap model for new energy vehicles has been explored, and NIO is self-sufficient in building battery swap stations, which are favored by users.
Aodong has built a power exchange platform to provide power exchange services for taxis, and some sites have already made profits. The battery swap mode reduces the cost of car purchase, solves the problem of charging, improves the efficiency of use, and is also conducive to the sustainable development of recycling enterprises.
On the basis of power battery replacement, recycling companies also push the battery replacement mode when using them in cascade. A typical example is a two-wheeler battery swap. Takeaway riders were the first to use lead-acid batteries, which often interrupted service because they could not be charged in time. The two-wheeled electric vehicle battery swap mode solved this problem very well, and was the first to commercialize and make profits.
In addition, in the process of battery recycling, it is often encountered that several tons of scattered batteries are not enough to fill a car and transport it back to the factory for processing.
Recyclers can choose to temporarily store in recycling outlets, save enough 30 tons, and then use a 15-meter cart to pull them away at one time. It is difficult to make a profit by building a branch by itself, and the annual operating cost is about 300,000. Therefore, co-construction and sharing of recycling outlets are the hotspots of recycling enterprises.
Material prices rise
The benefits of battery recycling are either cascade utilization or the value of material recycling.
Before 2021, the recycling and processing of lithium iron phosphate batteries can be used for cascade utilization, but it is a common phenomenon in the industry to lose money for recycling. Most companies are reluctant to recycle, and there have been cases where a few hundred yuan per ton is even given away for free, and the freight is self-care.
At the end of 2020, the price of lithium carbonate was still at a historical low, and it began to rise in 2021, soaring from 50,000 yuan/ton to 350,000 yuan/ton at the end of the year. As of February 17, 2022, the average price of lithium carbonate exceeded 430,000 yuan/ton.
As a result, the recycling price of waste lithium iron phosphate batteries has also risen, and the price of aluminum shell batteries has been 15,000 yuan/ton from about 2,000 yuan/ton in early 2021 (excluding tax and freight).
Obviously, if material prices continue to rise, it will boost the earnings of the power battery recycling business. So what is the price trend of battery materials? The price of battery materials is basically skyrocketing. We mainly look at lithium carbonate and cobalt.
There are three main reasons for the rise of battery-grade lithium carbonate in 2021.
First, the sales of new energy vehicles have doubled beyond expectations, and the supply of imported resources is insufficient, and Chinese smelting enterprises cannot produce at full capacity.
Second, the lithium extraction capacity of the salt lake is affected by the production reduction in winter, the equipment maintenance period and the stockpiling at the end of the year, and the supply is reduced.
Third, 52% of the world’s proven lithium reserves are in Chile, where Chilean President Boric won the election at the end of 2021, he focused on social change, promised to increase mining royalties and corporate taxes, and increase the cost of mining.
In addition, the momentum of new energy vehicles will not decrease in 2022. Some experts predict that the sales target of 5 million vehicles in 2025 will be achieved ahead of schedule this year, and it may hit 6 million vehicles. Lithium battery energy storage is also developing rapidly, and the demand for lithium battery is likely to exceed that of electric vehicles in the future.
On the supply side of lithium carbonate, many new projects will not be put into production until the second half of 2023 at the earliest. Therefore, there is a high probability that the price of lithium carbonate will continue to rise this year and remain at a high level.
The distribution of global cobalt ore resources is concentrated, mainly in the African Congo (DRC). China’s cobalt resources are very scarce, and ternary lithium batteries mainly recycle cobalt and nickel. Now the purchase price of waste ternary soft-package batteries (523 system) is close to 40,000 yuan/ton, and it is still the darling of recycling companies.
The price of cobalt fluctuates sharply and periodically. In the first quarter of 2018, the estimated price reached a historical high of 680,000 yuan/ton, and then fell sharply, falling to 340,000 yuan/ton by the end of 2018.
The main reason is that the growth rate of new energy vehicles slowed down after May 2018, and the demand was lower than expected. At the same time, starting from the second quarter, the production increase plan of cobalt ore was gradually realized, and the supply rose sharply.
In 2019-2020, the cobalt price fluctuated and adjusted, maintaining a low range of 200,000-300,000 yuan/ton. In 2021, the demand for raw materials will be tight, and the price of cobalt will continue to rise to more than 400,000 yuan. As of February 17, 2022, electrolytic cobalt will rise to 530,000 yuan/ton.
The African Congo (DRC) itself is a politically turbulent country, and its logistics capacity is not developed. Fortunately, the share of lithium iron phosphate batteries is gradually expanding, and the application of 811 low-cobalt system batteries has increased. The demand for cobalt resources is not as urgent as lithium, which may remain at 50 this year. -600,000 yuan / ton fluctuated at a high level.
The price of recycled ternary battery black powder in the market is mainly calculated based on cobalt content, nickel content and cobalt price coefficient. Cobalt is in the high range, the price coefficient is also high, and the recycling value of ternary cathode black powder is also increased accordingly, which is good for the development of the industry.
The high price of materials is one of the prerequisites for the operation of recycling enterprises. Recently, there has been news that in some scenarios, the price of old batteries is not inferior to new batteries, because recyclers value the value of material recycling.
Conclusion
Therefore, in terms of policies, it is necessary for the state to establish a supervision and punishment mechanism, launch a plan to include used power batteries in the “Hazardous Waste List”, and gradually implement the management of waste power battery recycling qualifications.
In terms of society, it is hoped that car companies will establish a battery recycling mechanism, or trade in old ones for new ones, and guide individual users to directly hand over the batteries owned by them to formal recycling companies, so as to reduce the links of middlemen.
In terms of technology, it is hoped that recycling companies will strengthen the research and development of process technology and equipment, pay attention to the development of power battery technology routes, plan the direction and focus of research and development, and commit to overall solutions for safe, environmental protection, refined and automated recycling.
The reason why the power battery recycling industry is interesting is mainly due to the uncertainty of the value of used batteries. Just like “betting on stones”, it is difficult for you to judge how much jade a stone contains and what the value of the jade is.
Of course, experienced battery recyclers can judge the value of used batteries as accurately as possible through certain methods and with the help of some tools to assist in analysis. In addition, it also depends on whether the recycling technology can really turn waste into treasure.