Home » lithium ion battery knowledge » Fast charging vs super fast charging – differences and working principle
Fast charging vs super fast charging - working principle and differences
With the continuous popularity of electric vehicles, various charging piles have appeared on the market, and charging technology is also constantly being developed. Following ordinary slow charging, there are fast charging and super fast charging.
What’s the difference between them? What is fast charging? And what about super fast charging? This article will compare the differences between fast charging vs super fast charging and how they work.

Charging principle of electric vehicle
First of all, we need to clarify a concept: the electricity used at home is alternating current, while the electricity output by the battery is direct current. The change from alternating current to direct current is called “rectification”; and the change from direct current to alternating current is called “inversion”.
When the AC charging pile charges the car, the alternating current enters the vehicle, and then the vehicle completes the “rectification” and voltage and current regulation work on its own.
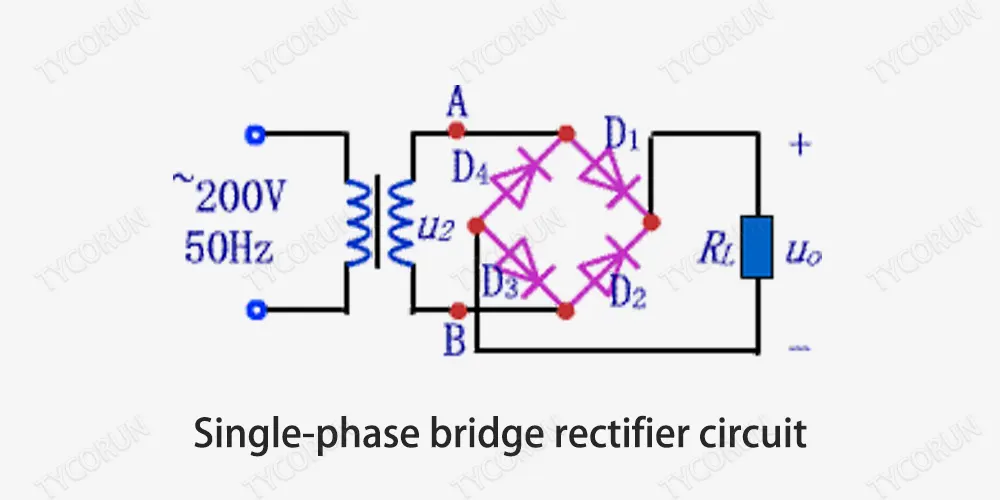
The electricity input to the vehicle from DC charging pile is already DC, and the voltage and current have been accurately adjusted, and it directly enters the lithium battery inside of the vehicle.
What power is a DC charging pile?
First of all, we need to understand what the power of a charging pile is. For example: charging power of 7KW means charging 7 kilowatt hours of electricity in one hour. So 60KW charging power means charging 60 kilowatt hours of electricity in one hour. In other words, the greater the power, the faster the charging.
Usually DC fast charging piles are composed of switching power supply modules. Taking China’s DC charging piles as an example, there is a unified standard for switching power supply modules. The power of a single module is 15KW, 2 modules in parallel makes 30KW; 4 modules in parallel makes 60KW, and so on.
The power of DC charging piles is doubled based on 15KW. For example: 15KW, 30KW, 45KW, 60KW…180KW, 240KW and 360KW (15KW is the lowest, and 360KW is the maximum). But in fact, most DC charging piles are 60KW. Basically, most of the large DC fast charging stations and fast battery charger in high-way service stations are 60KW. In some public parking lots, there are also some 30KW level DC charging piles.
What is fast charging vs super fast charging
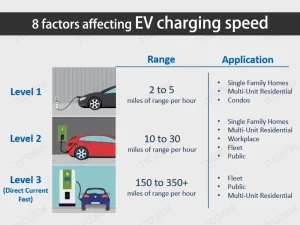
According to the different charging speed, the charging pile is divided into: slow charging, fast charging, and super fast charging.
AC slow charging:
The AC charging pile interacts with the vehicle, inputs the AC power from the grid into the slow charge port of the electric vehicle, converts the alternating current into direct current through the car charger, and then inputs the battery to complete the charging.
The average electric vehicle takes six to eight hours to complete a slow charging process. Although the current plug-in hybrid models can be connected to an external power supply to charge the vehicle, they are basically limited to slow charging.
DC fast charging:
The fast charging pile is called DC charging pile, the shape is similar to a refrigerator, and the volume is larger compared to slow charging pile. The charging principle is to use the charging interface of DC charging pile to directly charge the battery after converting alternating current into direct current.
Such charging piles often exist in high-way service stations or underground garages of large shopping malls. The power of DC fast charging piles is generally about 60kW, and in recent years, it has even reached 120-150kW. Generally, a charging ratio of more than 1C is considered to be fast charging. 1C refers to the full capacity of a battery, and 1C charging means that it takes 1 hour to fully charge the battery.
DC super fast charging:
When compare fast charging vs super fast charging, they are both DC charging. The volume of super charging pile is larger, and it contains many precise parts, so the production cost is higher.
Comparing fast charging vs super fast charging, its power is generally greater than 200kW, makes the charging speed extremely fast. Usually a super fast charging process is finished in half an hour to an hour, but the charging cost is also higher comparing fast charging vs super fast charging.

How super fast charging works
Technically speaking, lithium batteries use lithium intercalation chemical reaction. During charging and discharging, lithium ions move back and forth between the positive and negative electrodes. When discharging, lithium ions are deintercalated from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, and when charging, lithium ions are embedded in the negative electrode from the positive electrode.
Super fast charging is to increase the flow and speed of ions and quickly embed lithium ions from the positive electrode into the negative electrode. There is no difference in the essence of the working principle between fast charging vs super fast charging.
The risk of super fast charging mainly comes from the fact that when lithium ions flow rapidly, it is easy to form concentration polarization phenomenon, that is, the rates inside and outside the electrode are different, thus destroying the chemical structure of the positive and negative electrode materials. At the same time, when charging with high current, the battery will heat up rapidly. An overheated operating environment is formed, inducing thermal runaway of the battery.
But it is all controllable with technology. As long as the chemical structure of the positive and negative electrode materials does not change during super fast charging, the lithium-ion battery can ensure long-term and multiple cycles and achieve an ideal working life.
In recent years, lithium-ion battery technology has made great progress. Both the stability of the positive and negative electrodes themselves and the BMS battery management system have been continuously improved. The risks of super fast charging can be technically avoided.

Fast charging vs super fast charging – charging time
If the battery is charged to 80% (usually when the battery is charged to 80%, the charger’s current must become smaller in order to protect the safety of the battery. After that, the charging process starts to slow down from 80% to 100%. Therefore, 80% is generally used for assumption), the normal slow charging on the market takes at least 6 hours.
Comparing fast charging vs super fast charging, fast charging takes basically about 40 minutes, and the actual operation may take an extra 10 minutes on this basis. And super fast charging can charge 80% in 30-40 minutes, and in 80 minutes it will be fully charged. So we can see that the charging time of fast charging vs super fast charging is actually very similar.

Slow charging vs fast charging – which one is better
Fast charging:
The charging time is short. The voltage of DC charging is generally greater than the battery voltage, so the AC power needs to be converted into DC power through a rectifier, which places higher requirements on the voltage resistance and safety of the power wheels battery pack.
However, if the charging speed is too fast, it may result in false display of battery capacity. However, this is not the biggest problem. The biggest concern is that fast charging may shorten the service life of the battery. For electric vehicles, the battery life depends on the life of the vehicle. After all, the price of the battery accounts for a large part of the cost of buying an electric vehicle.
The reason why fast charging shortens the battery life is that the current generated by fast charging is larger than that of slow charging. Therefore, comparing fast charging vs super fast charging, the battery will generate high temperature during the charging process, and the high temperature will accelerate the aging of the battery, thus shortening the battery service life.
In serious cases, it will even cause the battery to be damaged, resulting in frequent breakdowns. If fast charging mode is applied to charge after long-term power loss, even the best battery cannot withstand such torment.
Slow charging:
Charge a battery at a lower speed will not cause the problem of false display of battery capacity compared to fast charging vs super fast charging. Moreover, the charging current and power of slow charging are smaller than those of fast charging, which not only reduces the heat and battery stress, but also helps extend the life of the battery. However, the charging time is much longer.
If the car owners are not in a hurry to use the car, it is recommended to choose slow charging compared with fast charging vs super fast charging. In addition, do not wait until the car is exhausted before charging. Try to find a charging pile to charge the car when there is still 20%-30% of the power. Of course, installing an AC charging pile in the own parking space shall be much more convenient.
Also, it is recommended to fully charge and discharge the electric vehicles at AC slow charging station once a month, which will help balance the battery and extend battery life. In low temperature environments, it is also recommended to use slow charging, which can make the battery have better use effect.

Will fast charging and super fast charging definitely reduce battery life?
As the production, sales and ownership of electric vehicles continue to increase, the vehicle-to-pile ratio remains high, causing car owners to spend a long time waiting for spare charging piles, and it is even difficult to find charging piles during holidays. Driven by “charging anxiety”, the era of fast charging of electric vehicles has arrived, and it has brought another anxiety:
Will fast charging and super fast charging reduce battery life?
What is really closely related to battery health is mainly thermal management and BMS (battery management system). 9 common factors that affect battery health include: battery current capacity, battery internal resistance, charge and discharge depth, charge and discharge rate, self-discharge rate, overcharge and over-discharge, number of cycles, charge and discharge current, and temperature.
Among them, in terms of charge and discharge rates, when charging at high rates, the temperature of the battery may rise too quickly, making thermal management more difficult and causing battery health to deteriorate. The BMS is called the protector of the battery, which can detect and analyze the battery status to avoid over-discharge and extend the battery life.
Using safe and reliable thermal management systems and BMS can effectively protect battery health. As long as car owners use the products and services provided by standard lithium battery manufacturer and develop good charging habits, normal fast charging and super fast charging will not cause great loss to the battery.
FAQs
Can electric hybrid vehicles use fast charging?
Fast charging is not available in electric hybrid vehicles. Because on electric hybrid vehicles, only one slow charging port is usually designed. This is mainly because the battery capacity of hybrid vehicles is small and does not need to be charged too fast. Moreover, slow charging can also extend the battery life, so for the absolute majority of hybrid electric vehicles with a range of 100 kilometers, slow charging is the most reasonable choice, and it can also save costs for manufacturers.
When should an electric vehicle get charged?
There is no standard answer to this question. Like mobile phones, it varies based on people’s anxiety levels. Generally speaking, if the car owners have their own charging pile at home, they can charge it at night. If they are are outside, it depends on the distribution density of charging piles/stations in the city. When 40% power is left, they need to consider charging; when 20% is left, they need to find charging piles quickly.
When charging an electric vehicle, can it be charged to 100%?
When charging electric vehicles, if it is slow charging, it can generally be charged to 100% or 90% without much impact. But if it is fast charging or super fast charging, it is recommended to stop charging when it reaches 80~90%. There is no need to fully charge the car every time for fast or super fast charging.